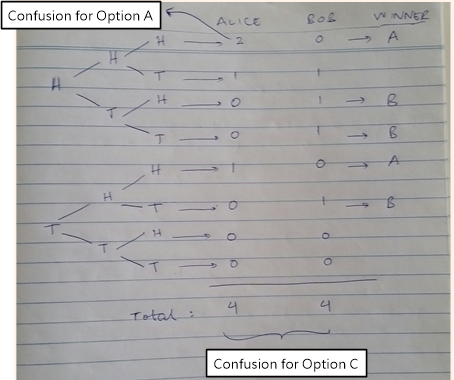
Recently, I wrote an article on why the Monty Hall problem has perplexed so many brilliant minds where I showed that it was a corner case between 1 open and 1 closed door, while the intuitive but wrong answer is close to the probability curve of 1 open door. Now a coin toss puzzle has appeared on Twitter [1] that has gone viral as it goes against our common intuition of probability and random sequences (such as a series of coin tosses). The puzzle goes as follows. The Problem Flip a fair coin 100 times—it gives a sequence of heads
Continue reading