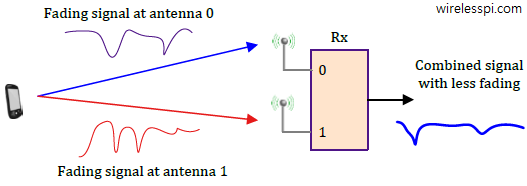
When computing approaches the physical limits of clocking speeds, we turn towards multi-core architectures. When communication approaches the physical limits of transmission speeds, we turn towards multi-antenna systems. What exactly are the benefits that led to scientists and engineers choosing multiple antennas as the foundation of 4G and 5G PHY layers? While having spatial diversity was the original incentive for adding antennas at the base stations, it was discovered in mid 1990s that multiple antennas at Tx and/or Rx sides open up other possibilities not foreseen in single antenna systems. Let us now describe three main techniques in this context.
Continue reading