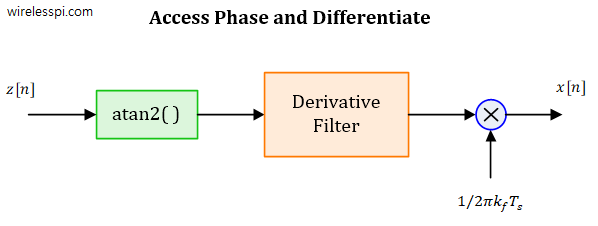
Frequency Modulation (FM) is as old as the history of wireless communications itself. The past few decades saw the rise of digital signal processing in all spheres of life that pervaded even the implementation of analog modulation schemes. Today many of the FM systems are built using discrete-time techniques instead of the conventional circuitry as described below. Frequency Modulation In digital communications, data is sent through altering a characteristic of an electromagnetic wave such as amplitude, frequency or phase in discrete steps (e.g., $M$ number of levels). Such systems are known as Amplitude Shift Keying (ASK), Frequency Shift Keying (FSK)
Continue reading