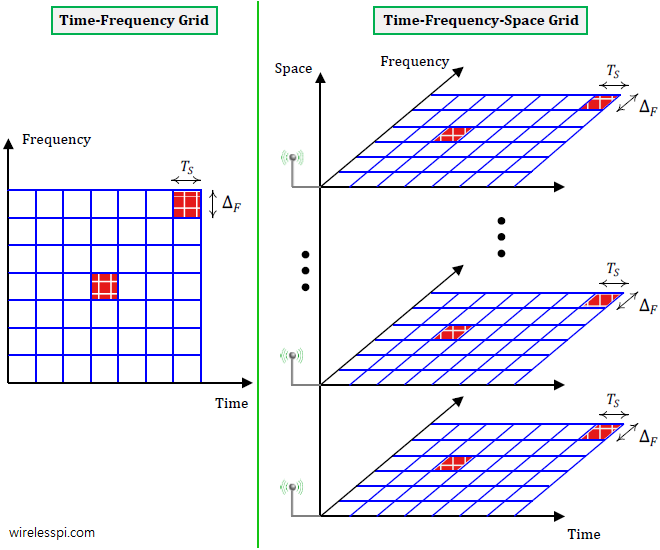
Once upon a time, an antenna was viewed as a simple device to transmit and receive an electromagnetic wave, much like a battery the sole purpose of which is to provide electrical power. A set of antennas, however, can be viewed from a new angle as follows. Sampling in Time Domain An Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC) is a device that samples an analog signal in time domain to create a corresponding sequence of numbers. Similarly, a Digital-to-Analog Converter (DAC) gets a sequence of numbers as an input to generate a reconstructed analog signal. As an example, a rectangular pulse shape is
Continue reading