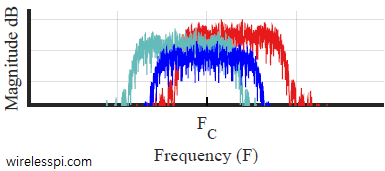
We discussed the idea of fading in wireless channels in a previous article. To understand different types of fading in the context of time variations, refer to the figure below that shows a multipath channel. Slow Fading A slow motion scenario is illustrated in the figure below where three multipath components are arriving with Doppler shifts FD,i from the carrier frequency. In this scenario, the magnitudes of FD,i are small and hence observe very little spreading of the cumulative spectrum. This can be understood by recalling that when two sinusoids with two different frequencies F1 and F2 are added, the
Continue reading