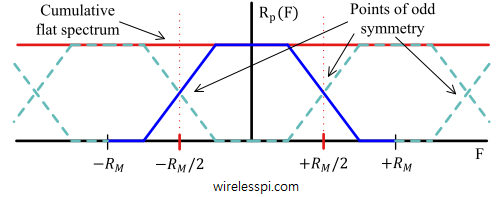
The Poisson sum formula was discovered by the French mathematician and physicist Siméon Denis Poisson. It has several applications in digital signal processing, among which our concern is the periodic summation of modulated pulses in digital communication systems. Assume that $p(t)$ is a pulse shape (or any continuous-time function if you are not familiar with digital communications) and $P(f)$ is its Fourier Transform. The pulse is sampled at a rate of $f_s$ to produce its discrete version $p(nT_s)$ where $T_s=1/f_s$ is the duration between two samples. The Poisson summation formula relates these two quantities as \begin{equation}\label{equation-poisson-sum-formula} \frac{1}{T_s}\sum _{k=-\infty}^{\infty} P\left(f+\frac{k}{T_s}\right) =
Continue reading