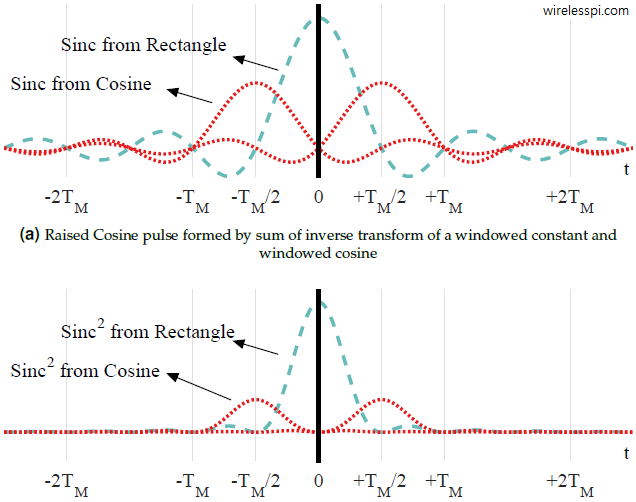
In the article on pulse shaping, we described the excess bandwidth, also known as roll-off factor, as the extra fractional bandwidth required to shape the spectrum. As it turns out, this excess bandwidth is also crucial for accomplishing timing synchronization in single-carrier systems due to its participation in generating spectral timing lines. Spectral Timing Lines Since a data stream consists of a sequence of 1s and 0s, the signal waveform is not a pure clock. Instead, a series of 1s and 0s appear in random order. The purpose of timing synchronization is to extract a clock out of this waveform.
Continue reading