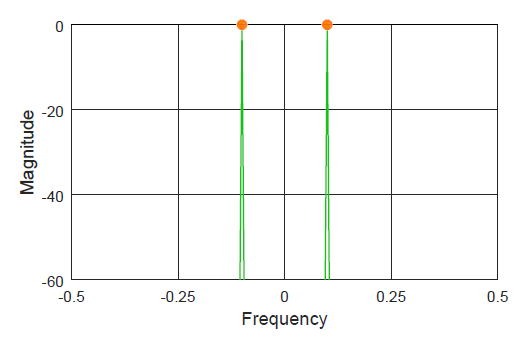
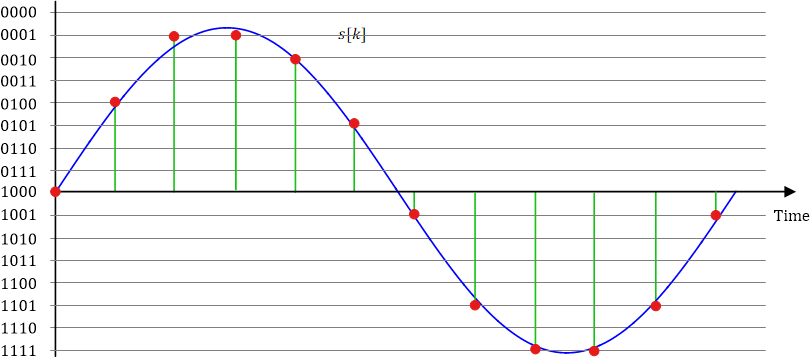
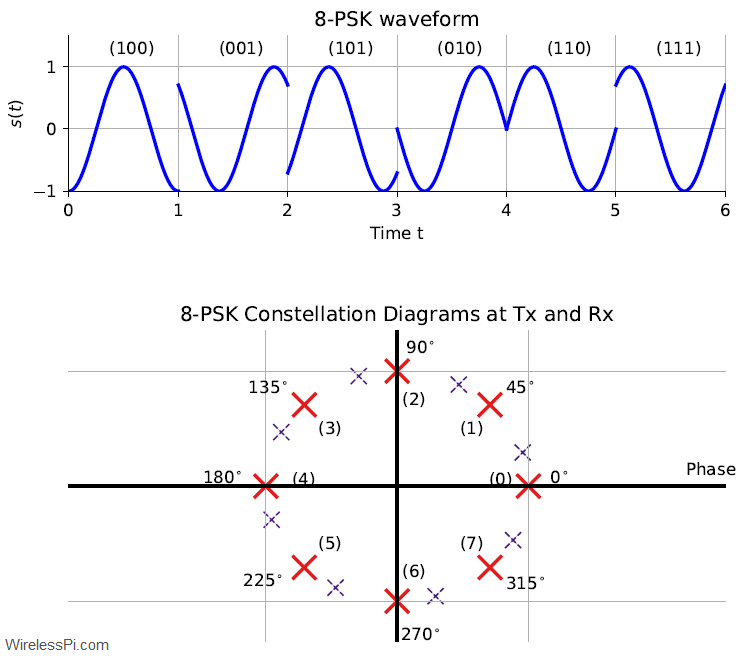
One of the most common questions DSP beginners have is how to generate the signals (particularly, sinusoids) and view their spectrum. They have a rough idea what time domain and frequency domain are about but struggle to construct the first few lines of code that open the gates towards a deeper understanding of signals. For this reason, I produce below an Octave (or Matlab) code that you can simply copy and paste to view and modify the results. Keep in mind that the code has been written for an explanation purpose, not conciseness or optimization. As you progress towards developing
Continue reading